
UTI St. John Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health problem affecting millions of people worldwide. UTI St. John is a type of UTI that can affect both men and women of all ages, although it is more common in women. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention of UTI St. John.
Symptoms of UTI St. John:
UTI St. John The symptoms of UTI St. John are similar to other types of UTIs, and they include:
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Passing small amounts of urine frequently
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Pain in the lower abdomen or back
- Feeling tired or shaky
- Fever or chills
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should consult your healthcare provider immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.
Causes of UTI St. John:
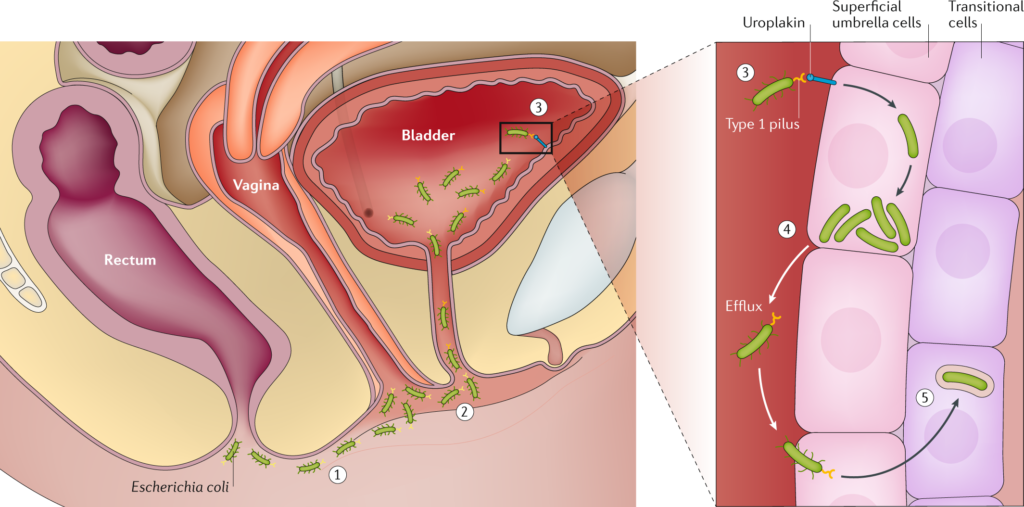
UTI St. John is caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). This bacterium is present in the digestive system and is usually harmless. However, it can cause an infection when it enters the urinary tract through the urethra. Women are more prone to UTI St. John because their urethra is shorter than that of men, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder.
Other risk factors for UTI St. John include:
- Being female
- Being sexually active
- Using certain types of contraceptives, such as diaphragms or spermicides
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having diabetes
- Having a history of UTIs
- Being pregnant
Treatment of UTI St. John:
The treatment of UTI St. John usually involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the appropriate antibiotics based on the severity of the infection, your age, and any underlying medical conditions you may have.
It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics prescribed, even if your symptoms improve before the medication is finished. Failure to complete the full course of antibiotics can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which can be more difficult to treat.
In addition to antibiotics, your healthcare provider may recommend pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, to help alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with UTI St. John. Drinking plenty of water can also help flush out the bacteria and reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention of UTI St. John:
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing UTI St. John:
- Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria from your urinary tract
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent the spread of bacteria
- Urinate frequently and completely to avoid the buildup of bacteria in your bladder
- Avoid using perfumed products in the genital area, such as sprays or douches, as they can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of infection
Use condoms during sexual intercourse to reduce the risk of transmitting bacteria from one partner to another
Avoid using diaphragms or spermicides if you are prone to UTIs, as they can increase the risk of infection
Conclusion:
UTI St. John is a common health problem that can cause discomfort and pain. It is caused by the bacteria E. coli and can affect both men and women. The symptoms of UTI St. John include pain or burning sensation during urination, frequent urge to urinate, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
UTI St. John How Its Work?
UTI St. John is a type of urinary tract infection caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). The urinary tract is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and its function is to remove waste and excess water from the body.
When bacteria such as E. coli enter the urinary tract through the urethra, they can multiply and cause an infection. Women are more prone to UTI St. John because their urethra is shorter than that of men, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder.

Once the bacteria have entered the urinary tract, they can cause inflammation and irritation, leading to symptoms such as pain or burning sensation during urination, frequent urge to urinate, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. The infection can also cause pain in the lower abdomen or back, fatigue, and fever or chills.
If left untreated, UTI St. John can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage or a bloodstream infection. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.
The treatment of UTI St. John usually involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the appropriate antibiotics based on the severity of the infection, your age, and any underlying medical conditions you may have. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics prescribed, even if your symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
If you want to get amazing benefits by using this link
In addition to antibiotics, your healthcare provider may recommend pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, to help alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with UTI St. John. Drinking plenty of water can also help flush out the bacteria and reduce the risk of complications.
To prevent UTI St. John, it is important to maintain good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back after using the toilet, urinating frequently and completely, and avoiding the use of perfumed products in the genital area. Using condoms during sexual intercourse and avoiding the use of diaphragms or spermicides if you are prone to UTIs can also help reduce the risk of infection.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, UTI St. John is a common health problem caused by the bacteria E. coli, which can lead to discomfort and pain. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery. Maintaining good hygiene and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing UTI St. John.

More Stories
What is Honda Lowers Bike Pricing in Pakistan
Transforming Global Communications: The Impact of Continuous Localization
Receive Financial Success by Working with CPA Queens